Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionising the way organisations handle repetitive, rule-based tasks across industries.
Every modern organisation has processes that can be automated profitably. The business operations encounter a daily struggle to complete tasks because of the repetitive work such as forwarding emails and tracking approvals, generating reports, and moving files, which consumes several hours throughout the week. RPA provides the answer to this problem.
Businesses can build automated workflows through Power Automate, which connect various applications and services, including Outlook, Teams, SharePoint, Excel, Power BI, and external third-party tools.
In this article, we showcase 13 real-world RPA examples drawn from client engagements and internal projects, selected for their business impact, level of adoption, and innovation.
For each example, we’ll outline:
RPA is more than just a cost-saving tool; it’s a strategic advantage that helps businesses run smarter, faster, and more reliably. By reducing human error, enhancing compliance, and enabling operations to scale, it empowers organisations to stay competitive in dynamic markets while freeing employees to focus on high-value, strategic work.
Invoice processing using RPA is the end-to-end automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks involved in handling invoices by deploying software bots that extract invoice data, validate information, route approvals, and initiate payments without human intervention.
We provided a similar solution for a company’s finance team that was overwhelmed with the manual handling of supplier invoices.
Every day, dozens of invoices would arrive via email, and the process to manage them was:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Download | The finance team manually opened each email, downloaded the attached invoices (PDF or Excel), and saved them to a shared folder. |
| Approval Routing | The team manually forwarded the saved invoice via email to the respective manager or project lead for approval, causing delays and confusion. |
| Updating Records | Once approved, the finance team manually updated the financial system or Excel sheets with invoice details; this was time-consuming and error-prone. |
Because of these manual steps, approvals were delayed, finance records were not always up-to-date, and supplier payments risked getting delayed, affecting vendor relationships.
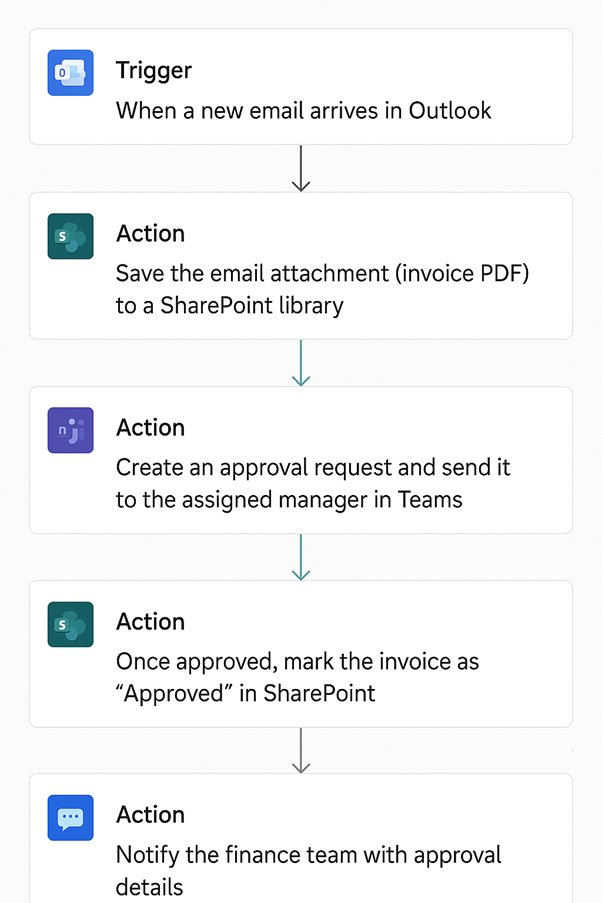
To address this, we automated the entire invoice process using Power Automate, SharePoint, and Microsoft Teams.
The new workflow worked as follows:
| Step | Action / Description |
|---|---|
| Email Capture | Power Automate flow monitors a shared “Invoices” mailbox. When a new email with an invoice attachment arrives, the flow captures the email and attachment automatically. |
| Invoice Storage | The attachment is extracted and stored in a dedicated SharePoint library with metadata (supplier name, date received, subject, etc.) for easy search and secure backup. |
| Approval Request in Teams | After saving, the flow sends an approval request in Microsoft Teams to the relevant manager, who can approve or reject directly from Teams. |
| Finance Record Update | Upon approval, the company’s finance system or SharePoint list is updated with the approval status, invoice details, and manager’s response. If rejected, finance is notified for follow-up. |
Automating the process saved hours of manual work, reduced approval delays with instant notifications, and centralised invoices in SharePoint for easy access. Digital logging ensured audit readiness, while faster approvals improved vendor satisfaction through quicker payments.
The diagram below shows the Power Automate steps we followed:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text from images, PDFs, or scanned documents into editable and searchable digital text. Instead of manually retyping information, OCR “reads” the characters on a page and translates them into machine-readable data.
For businesses, OCR speeds up document processing, reduces errors, and makes records easier to store, search, and analyse, for example, turning stacks of invoices into structured data for accounting systems.
We solved this problem for a company’s sales team that was responsible for handling customer order confirmations. These confirmations arrived daily in PDF format from different clients.
The workflow table is shown below:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Extraction | Team members had to open each PDF one by one. |
| Data Entry | Manually typed customer name, order number, product details, quantity, and price into an Excel tracker. |
| Verification | Another team member had to double-check entries due to frequent mistakes like wrong numbers or missing items. |
This process was highly time-consuming, taking several hours each day. It also led to human errors, which created downstream issues like incorrect stock allocation or invoicing mistakes. The sales team was spending more time on data entry than on actual selling and customer engagement.
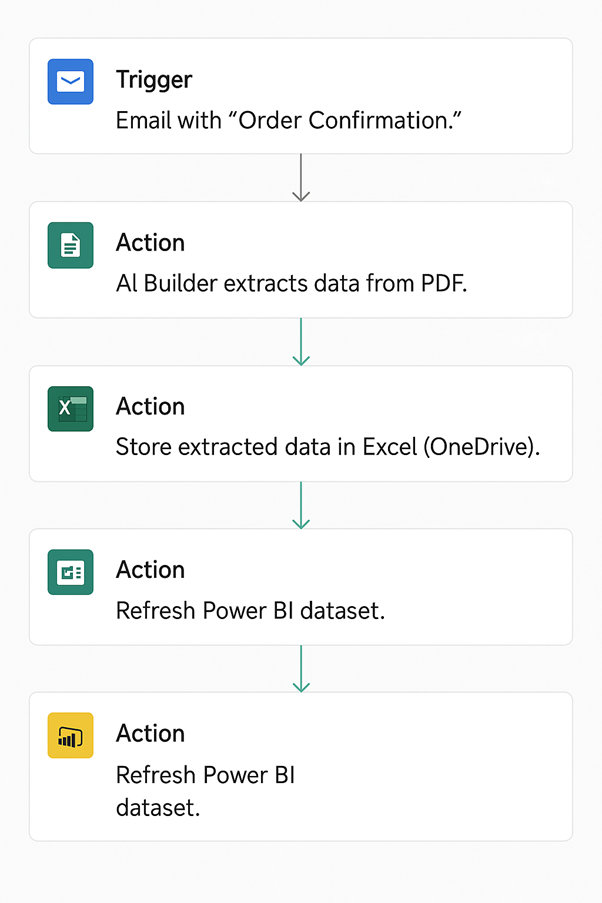
To overcome this, we introduced an automated PDF data extraction solution using Power Automate and AI Builder:
| Step | Action / Description |
|---|---|
| PDF Capture | – Flow monitors incoming emails for attached order confirmation PDFs. – Each PDF is auto-saved to SharePoint for processing. |
| AI Builder Extraction | – AI Builder form processing extracts structured details (customer name, order ID, product, quantity, amount). – Model is trained with samples to recognise varied layouts. |
| Excel Storage | – Extracted data is written into a central Excel file or SharePoint List for sales tracking. – No manual typing required. |
| Notifications & Validation | – Sales team receives Teams/Outlook notification when orders are logged. – Team only needs to review and validate, not type data from scratch. |
The AI‑powered solution saved hours of manual work, improved accuracy, sped up order processing, scaled to handle hundreds of PDFs daily, and freed the Sales team to focus on customer relationships instead of admin tasks.
To execute this, we followed the steps below:
RPA automates the employee onboarding process by enrolling new hires, scheduling meetings, induction sessions, sending automated messages and emails detailing their roles and responsibilities.
Additionally, RPA can automate creating employee accounts across multiple systems, granting leave requests, setting up email addresses, and preparing workstations by installing the required software.
We worked with a company that had no centralised system for managing employee leave requests.
The leave request process was completely manual, as shown in the table below:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Request Submission | Employees emailed their managers or the HR team when they needed to leave. |
| Tracking | HR maintained an Excel sheet to track requests, opened each email, checked for duplicates, updated the sheet, and informed the manager. |
| Approvals | Managers replied by email to approve or reject requests, and HR updated the sheet again. |
Because everything depended on emails and manual updates:
-Many requests were missed or forgotten.
-Employees were unsure if their leave was approved.
-HR wasted a lot of time maintaining the Excel sheet.
-Managers had no easy way to view team availability at a glance.
This caused frustration for employees, workload issues for HR, and even cases of overlapping leaves that disrupted project planning.
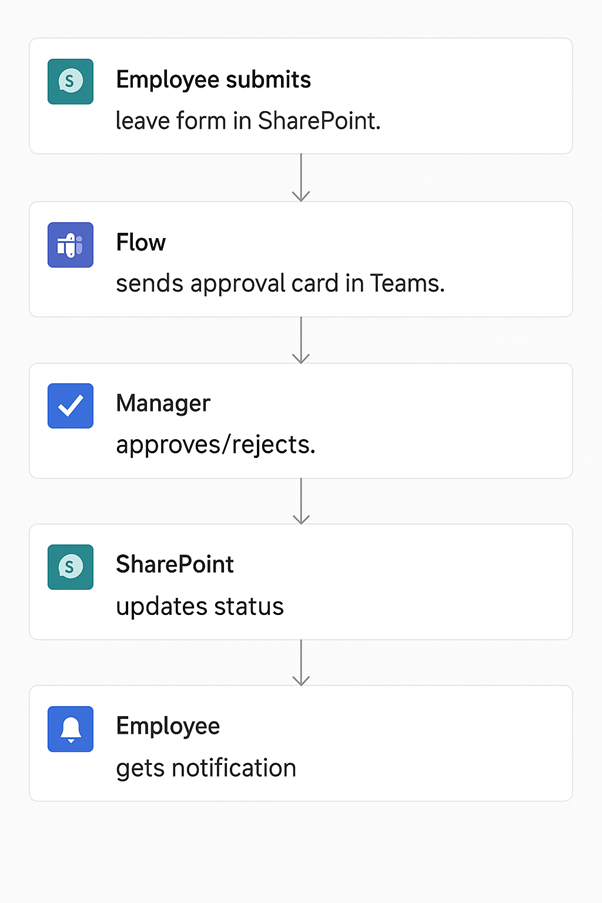
We implemented the automation as described in the table:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralised Leave Request Form | Employees submit leave requests through a SharePoint form capturing date range, reason, and leave type, eliminating email dependency. |
| Approval Workflow | Power Automate triggers an approval request to the employee’s manager via Teams or Outlook for easy one-click approval or rejection. |
| Automatic Tracking | Approved requests are updated in the SharePoint list with status and comments; HR accesses a real-time dashboard without manual Excel updates. |
| Notifications | Employees receive instant approval/rejection notifications; managers get reminders for pending requests. |
Automating leave requests ensured nothing was missed, gave HR and managers clear visibility in a central dashboard, saved time by removing manual tracking, improved employee satisfaction with timely updates, and supported better planning through full team availability insights.
The Power Automate process shown below:
The manual effort that has traditionally been associated with planning can be eliminated by RPA, which could change the way in which organisations manage scheduling. Instead of relying on managers to manually gather data, check availability, and align resources, RPA applies predefined rules and business logic to automatically generate accurate schedules.
For example, automation can generate weekly sales dashboards, match employee availability with workload, ensure compliance with labour regulations, and dynamically adjust schedules based on leave requests or sudden demand changes.
Vidi Corp handled a similar project for a company whose management team relied on Power BI dashboards to track weekly sales performance. While the dashboards contained all the necessary insights, there were practical challenges as shown in the table below:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Barriers | Executives often didn’t log into Power BI due to time constraints or unfamiliarity with the tool. |
| Delays | The sales team manually exported data or screenshots from Power BI and emailed them weekly. |
| Inconsistency | Different managers received slightly different report formats depending on who prepared them. |
| Dependency | If the person responsible for sharing reports was unavailable, leadership missed critical updates, causing frustration at the top level. |
This led to frustration at the leadership level, where timely, consistent updates were critical for decision-making.
We automated the entire reporting process by setting up a scheduled Power Automate flow that connected with Power BI.
The table below shows our implementation process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Scheduled Trigger | A flow was set to run automatically every Monday morning. |
| Power BI Report Export | The flow used Power Automate’s Power BI connector to export the latest weekly sales report as a PDF or Excel file with dynamic filters. |
| Email Delivery | The exported report was attached to an email and sent to all relevant executives with a summary and a link to the live Power BI dashboard for further analysis. |
This resulted in automated reporting delivered consistently, on‑time insights straight to executives’ inboxes, saving the sales team hours of manual work, enabling quick leadership decisions, and scaling easily to other departments.
The process we followed is shown in the diagram below:

Social media monitoring using automation means setting up tools or workflows that continuously track what’s being said about your brand, products, competitors, or industry across social platforms without you manually searching every day.
It’s essentially your 24/7 “radar” for online conversations, helping you respond faster, protect your reputation, and spot opportunities early.
We recently helped the marketing team, which was responsible for monitoring the company’s online reputation and customer engagement. A key part of this was tracking Twitter (Now X) mentions.
However, the process they followed was inefficient, as shown in the table below:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Monitoring | Team members had to log into Twitter multiple times daily and refresh feeds to check for company mentions. |
| Delayed Responses | Mentions outside working hours or missed checks resulted in customer questions or complaints going unanswered for hours or days. |
| Missed Opportunities | Positive mentions from customers or industry leaders were sometimes overlooked, missing chances for engagement. |
This created a gap in customer communication and harmed the company’s responsiveness on social media.
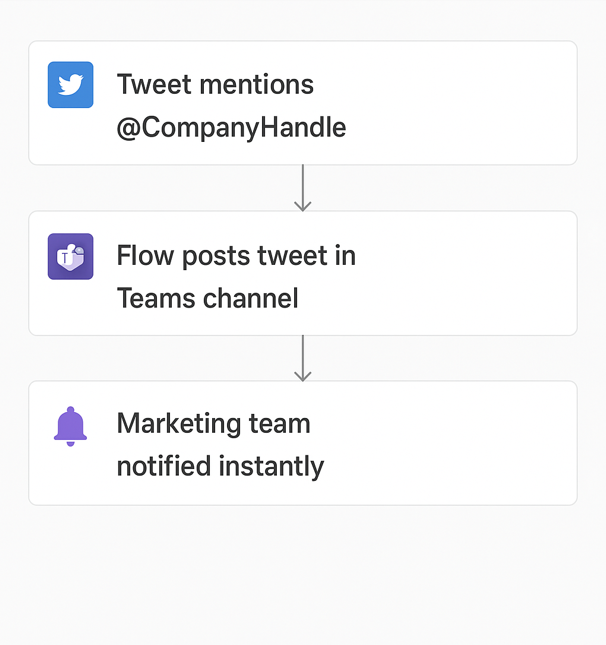
To solve this, we built a real-time notification flow connecting Twitter and Microsoft Teams using Power Automate:
The table below highlights the process we followed:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Twitter Trigger | The flow triggers automatically whenever the company’s Twitter handle is mentioned in a tweet. |
| Data Capture | The tweet content, user details, and timestamp are captured automatically along with a direct link to the tweet. |
| Teams Notification | A formatted message with the tweet details is posted into a dedicated “Social Mentions” channel in Microsoft Teams. The marketing team can view and respond directly from Teams. |
This resulted to real‑time Twitter mentions in Teams, which gave the marketing department instant awareness, faster customer engagement, a stronger brand image, centralised visibility for the whole team, and a scalable setup for broader social listening.
The steps we used to automate this procedure are below:
File organisation using Robotic Process Automation (RPA) means automating repetitive tasks like sorting, categorising, renaming, transferring, and backing up files across multiple systems or locations. Bots can automatically move documents to designated folders, apply naming conventions, delete outdated files, and handle scheduled backups, ensuring consistent and efficient file management with minimal manual effort.
One of the similar problems we solved is for an organisation where the employees across departments were saving files into a single shared folder. Over time, the folder became cluttered with hundreds of documents, spreadsheets, PDFs, images, presentations, and more.
Here is the information arranged into a table:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Unstructured Storage | Files were dumped into one location without naming conventions or organized subfolders. |
| Time Wasted | Employees spent excessive time manually searching through disorganized files. |
| Errors | Important documents were often overlooked or misplaced, causing work delays. |
| Frustration | Staff were frustrated by wasted time locating files instead of focusing on their actual work. |
This lack of structure was slowing productivity and reducing collaboration efficiency.
We automated file organisation with a Power Automate flow that sorted documents the moment they were uploaded:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| File Trigger | A flow was created to monitor the shared folder for newly added files. |
| Automatic Categorization | The flow categorised files based on type (PDF, Excel, Word, Image, PPT) and optionally captured metadata like uploader and date. |
| Move to Subfolders | Files were automatically moved to designated subfolders (e.g., Invoices, Reports, Presentations) instantly without manual sorting. |
| Notification (Optional) | Employees could receive a notification via Teams or email confirming where their file was stored, simplifying retrieval. |
Automated file organisation ensured documents were instantly sorted, easy to find, and less likely to be misplaced, boosting collaboration, reducing errors, and scaling effortlessly across projects or departments.
The steps we followed are shown in the diagram below:

RPA bots can extract order customer details from emails or web forms, check inventory availability, validate order information, and process payments efficiently. They also generate shipping labels, update tracking systems, send automated order confirmations to customers and collect feedback.
Vidi Cop worked with a support team that wanted to collect customer feedback after resolving support tickets. Initially, the whole process was done manually as described in the table below:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Follow-up | Team members had to remember to draft and send survey emails to customers after ticket closure. |
| Inconsistency | Survey emails were sometimes sent late, in the wrong format, or missed entirely. |
| Low Response Rate | Many customers never received surveys due to the lack of a standardised process, causing inaccurate management feedback. |
| Poor Visibility | Survey responses were scattered across emails and spreadsheets, making tracking and analysis difficult. |
This meant the company had no reliable way to measure customer satisfaction and improve support services.
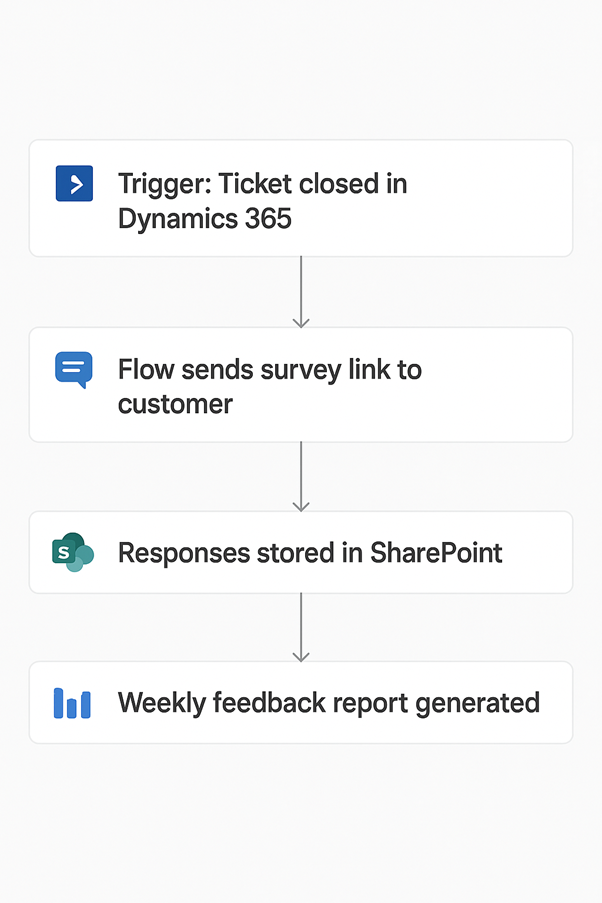
We automated the entire feedback process using Microsoft Forms and Power Automate:
The table below explains the details:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Survey Creation | A customer satisfaction survey was created in Microsoft Forms, including questions on satisfaction, issue resolution, and comments. |
| Automated Trigger | A Power Automate flow was triggered when a support ticket was marked resolved in the system. |
| Survey Email | The flow sent a standardised, professional email automatically to customers with a personalised message and a survey link. |
| Response Collection | Survey responses were captured automatically in Excel Online or a SharePoint List for centralised tracking and analysis. |
| Management View | Management could view survey trends and analytics easily through Power BI dashboards. |
Automated survey emails after every resolved ticket ensured consistent outreach, boosted response rates, centralised feedback for easy analysis, saved the support team time, and gave managers clear insights to improve processes.
The diagram below depicts the entire process:
Automating task creation turns incoming requests into actionable work instantly, with no manual entry, no missed details. Every email, form, or trigger becomes a neatly assigned task in your project tool, giving teams more time to focus on delivery instead of admin.
This automation frees employees from mundane work, allowing them to focus on strategic, value-added activities.
We created an automation for project managers who often receive new work requests or updates by email. Turning these into actionable tasks was a manual, repetitive process:
The table below highlights the initial steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Reading | Project managers had to open each email and interpret the work request. |
| Task Creation | Managers manually opened Microsoft Planner, created a new task, copied details from email (subject, due date, description), and assigned it to the correct person. |
| Time Wasted | This repetitive process consumed significant time, especially with many requests daily. |
| Risk of Errors | Details were sometimes missed or entered incorrectly, causing confusion and delays in project execution. |
This slowed down productivity and created frustration for managers who wanted to focus more on managing projects than on administrative work.
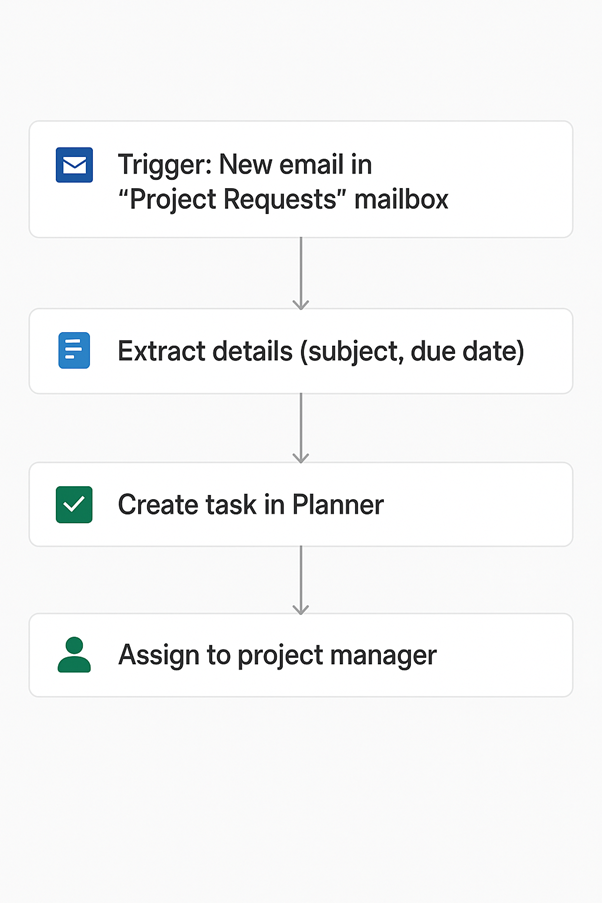
We automated task creation directly from incoming emails using Power Automate and Microsoft Planner:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Trigger | A flow triggers whenever a new email arrives in the “Project Requests” mailbox. |
| Data Extraction | The flow captures key details from the email: Subject line → Task Title, Body → Task Description, Due date → Task Deadline |
| Planner Task Creation | A new task is automatically created in Microsoft Planner and assigned to the relevant project manager or team member. |
| Email Attachment | The original email is attached to the task for easy reference, ensuring no details are lost. |
| Notification | The assigned individual receives an instant notification in Teams or Planner about the new task. |
The task creation automated from emails saved managers time, improved accuracy, sped up assignments, centralised tracking in Planner, and boosted productivity by freeing them to focus on planning and execution.
The steps we followed in automating the tasks:
An Employee Work Hour Tracker is a tool that helps businesses accurately monitor staff attendance and working hours without relying on manual timesheets.
It automatically records when employees start and finish work, tracks breaks, and calculates overtime. This ensures fair and accurate payroll, reduces human error, and saves time for managers.
It also helps with compliance by keeping reliable records and gives the business managers real-time insights into productivity and scheduling.
We worked with an organisation where the managers needed visibility into when employees were logging in and out each day to understand work patterns better and ensure attendance compliance.
The original process relied on employees manually recording their login and logout times in a shared sheet, as shown in the table below:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Forgetfulness | Employees often forgot to record their times, leading to missing or inaccurate data. |
| Manual errors | Even when they did remember, entries were sometimes wrong or incomplete. |
| Time wasted | HR and managers had to chase employees to correct or fill in missing information. |
| No real-time view | Management lacked an accurate, centralised, and real-time record of working hours. |
This made it hard to track productivity, address attendance issues, or generate weekly/monthly reports.
We automated the login/logout tracking process by leveraging Microsoft Teams activity with Power Automate, as shown in the table below:
| Step | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger on Teams Activity | Login/Logout Capture | Employee sign-in to Teams was recorded as login time, and going offline/inactive was captured as logout time. |
| Data Storage | SharePoint Logging | Each login and logout entry was automatically stored in a SharePoint list, including employee name, date, login time, logout time, and duration. |
| Report Generation | Automated Reporting | Daily and weekly summaries were generated from SharePoint data and shared with managers as Excel reports or via a Power BI dashboard. |
| Notifications (Optional) | Activity Alerts | Managers could receive alerts if an employee had no login activity during scheduled work hours. |
The new system automatically captures accurate attendance data in real-time, eliminating the need for employees to log hours. This provides managers with instant visibility into work activity, enables clear productivity tracking, and reduces HR’s effort in correcting records.
The image below shows the Power Automate steps we followed:
Social media scheduling is the process of using automated workflows to plan, queue, and publish posts across platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter (X), or Facebook at set times.
Instead of manually posting, you create a flow that pulls content from a source (e.g., SharePoint, Excel, or a content calendar), schedules it, and automatically publishes or queues it through connected apps.
For businesses, this means consistent posting, time savings, and reduced human error, while giving marketing teams more control over timing and campaign coordination.
Vidi Corp helped a marketing team with scheduling LinkedIn posts in advance to keep the company’s social presence consistent.
The table below highlights the challenges they faced:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| No native scheduling | LinkedIn does not provide advanced scheduling features without external tools. |
| Cost concerns | Paid third-party tools (like Hootsuite or Buffer) were considered too expensive for their needs. |
| Manual effort | Posts had to be created and published manually at the right time, which was inefficient and prone to delays if team members were busy. |
| Missed opportunities | Sometimes posts were not published on time, reducing engagement and campaign effectiveness. |
The solution we provided includes designing a custom LinkedIn scheduling system using SharePoint + Power Automate:
1. Content Storage in SharePoint
2. Scheduled Flow
3. Publishing to LinkedIn
4. Team Notification
By centralising posts in SharePoint and automating publishing through Power Automate, the company saved costs on external tools, ensured consistent and timely LinkedIn activity, reduced manual effort, and improved team collaboration with a clear, shared campaign schedule.
Website scraping means automatically extracting data from websites. An RPA bot can go through the website pages one by one and extract the relevant data from pre-defined placeholders.
Many website scraping projects involve bypassing anti-scraping defences like captchas or Cloudflare. Websites have those since they want to reserve themselves to genuine visitors instead of bots. Those defences can be worked around by using a proxy server, which changes the IP address of each website request and helps simulate traffic from multiple genuine users. As a result, it looks like the requests that you send come from many different users instead of one, and you don’t trigger the defences.
Sometimes companies need to do a one-off data scrape from a website, for example, when they are doing market research. Other web scraping processes are scheduled to run once a week or a month, for example when companies are refreshing their reporting.
It is also possible for web scraping to happen in real time. For example, we have worked with an e-commerce platform that aggregates product offerings from Nike, Adidas, Puma and other retailers. This platform scrapes the websites of all of these retailers to compare the prices per product and suggest the lowest price to the website visitor.
At Vidi Corp, we have experience with 2 approaches to web scraping.
Power Automate Desktop enables users to create bots that automate mouse clicks and keyboard strokes. As a result, a bot can open a website and perform the same operations as a person would: open a website, navigate to a relevant page, etc.
The video below shows an example of a Power Automate Desktop bot that we created. You can see the messages like “Flow X is running” when we launch it and “Flow X completed successfully”.
This web scraping method is pretty simple to set up, but it tends to work slowly with large volumes of data. It also has limited capabilities for working around the website’s anti-scraping defences.
If you want to scrape a large volume of pages, this approach would work better for you. It works faster because the script doesn’t have to use the
Our approach typically looks like this:
This approach offers several advantages:
1. The scraping operations execute very fast, which is essential for scraping large data
volumes. You will find that scraping through Power Automate or browser extensions
usually works a lot slower.
In one of our projects, we tried scraping 2M rows of data using Power Automate. The
expected run-time was 2 months. We then pivoted to using Python, and the script extracted
all the 2M rows perfectly in 3 hours.
2. The speed of web scraping also improves the stability of the system since the risk of
facing timeout errors is much less.
3. Coding the scrapers in Python gives a lot of flexibility to work around anti-scraping
defences like Cloudflare, captchas, etc.
Here is a verified review from a client who we helped scrape data fromseveral online marketplaces.
RPA in inventory management helps to automate tracking of inventory levels, reorder points, and even place orders to suppliers when those reorder points are reached. This helps the businesses to avoid stockout periods and optimise the overall supply chain.
Many businesses also send their inventory to the client site to rent it or perform a project. In this case, RPA in inventory management can help to track the location of the inventory and its status.
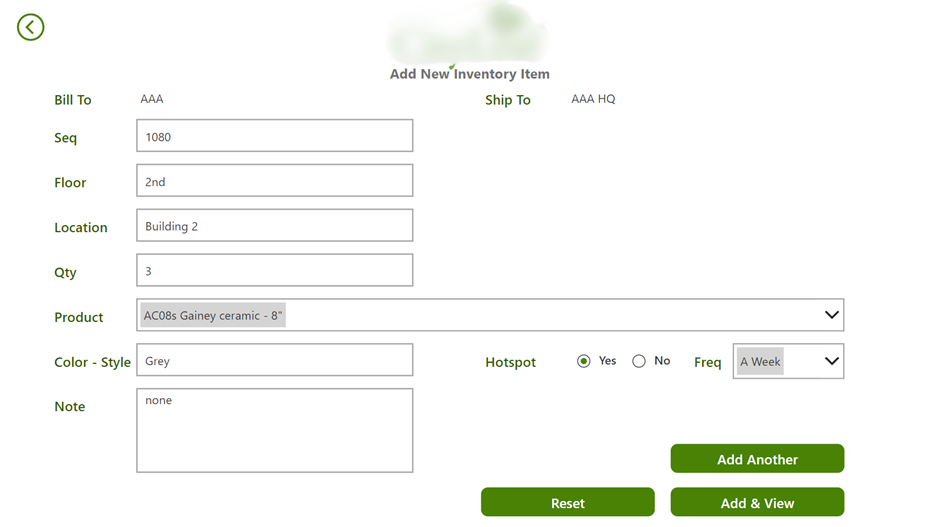
For example, we have worked with a company that rents office plants to corporate clients. Before our inventory management RPA project, they had several pain points:
To solve this problem, we created an inventory management Power App. The warehouse staff can place orders through the app, which then automatically generates freight labels through integration with a shipping software called Ship Station.
They can also use the app to scan barcodes in the warehouse, which automatically updates their inventory levels data and schedules deliveries for customers.
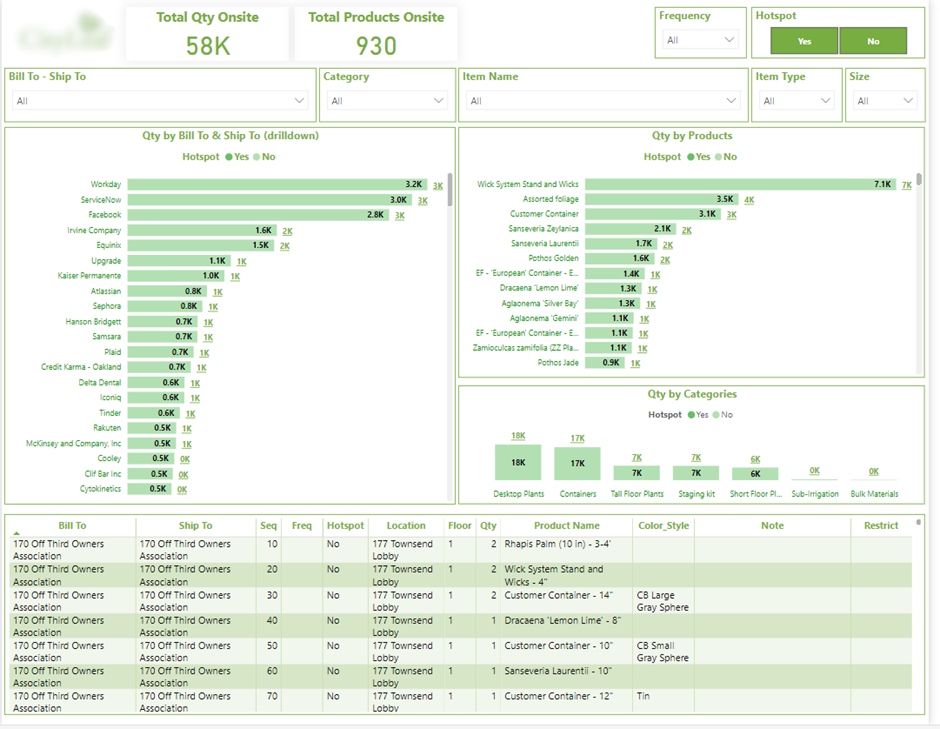
We have also built a Power BI reporting solution that shows how many items are currently with each customer and where they are located at all times. Knowing their actual stock quantity and location helps them to stay in control.
Data Migration in RPA involves using bots to extract the data from legacy systems and insert it into new platforms. Migrating this data manually takes a lot of time and poses challenges like migrating user permissions. RPA can help to migrate both the data and user permissions automatically, reducing the risk of data breach due to manual errors.
As RPA consultants, we mainly work on SharePoint data migration when customers move from SharePoint 2013 to SharePoint Online. We used a data migration tool called Sharegate to help us move all the files to the new environment. Sharegate also allows us to migrate user-level file permissions, helping us ensure the security of our data.
One common challenge in data migration projects is handling the volume of data presented. For example, in one of our projects, we were migrating 10 GB-worth of files to SharePoint Online, and initially, the migration was taking a long time. We worked around it by splitting our file transfer into multiple smaller streams, which executed without any timeout errors.
Here is a review from Hakim Group who we helped migrate to SharePoint Online. Their SharePoint site is now used by 1000+ employees and includes smart automations built in Power Automate.
If you found any RPA examples that are relevant to you, our RPA consultants can help you achieve the same automations. Simply contact us today and we will help you achieve similar automation quickly and efficiently.
From automated approvals to real-time reporting and scheduled content, teams gain time, accuracy, and efficiency. RPA empowers workers and business managers to focus less on routine and more on creating real business value.
RPA uses software bots to automate high-volume, repeatable tasks previously performed by humans, enabling businesses to scale processes efficiently and with fewer errors
The common examples include invoice processing, data migration, and social media scheduling
RPA can reduce operational costs by 25% to 80% each year.