
Financial Business Intelligence is the use of data analytics and visualization to turn raw financial data into clear insights that enhance financial management and operational performance. It leverages business intelligence tools to automatically extract, transform, and visualize data, presenting the results through a series of management reports
The main benefit of financial business intelligence is uncovering insights that drive revenue growth or cost reduction. Implementing business intelligence in finance also helps to save dozens of hours per month by automating the data extraction and transformation processes.
Generally speaking, financial BI can be divided in 3 big areas: accounting analytics, financial analytics and business intelligence in financial services. Our BI consultants have case studies in all 3 of these areas which we will show in this article.
I worked as a Financial BI Analyst at Autodesk for 3+ years, where I developed Power BI reports for the CFO, Financial Directors, and VPs of Finance. My team and I also delivered 100+ financial dashboards for clients such as Google, Teleperformance, and Heineken.
Based on my experience the financal business intelligence process includes the following steps:
Throughout these steps, maintaining data accuracy and establishing data governance policies are essential to ensure high data quality, integrity, and security for reliable BI. Poor data quality can compromise the reliability of financial insights, making it critical to validate, cleanse, and govern business data throughout the process.
Financial Business Intelligence (BI) is the cornerstone of modern financial management, empowering organizations to transform raw financial data into actionable insights. By leveraging advanced business intelligence tools, finance teams can efficiently gather, process, and visualize complex financial data, providing a clear picture of the organization’s financial health. This process enables finance professionals to identify trends, monitor key financial metrics, and make informed decisions that drive financial performance.
Implementing financial business intelligence allows companies to move beyond traditional reporting methods, offering a dynamic approach to analyzing financial business operations. With the ability to visualize financial data in real time, organizations can quickly spot opportunities for revenue growth, address potential risks, and optimize resource allocation. Ultimately, financial BI equips finance teams with the insights needed to stay competitive, adapt to changing market conditions, and support sustainable business growth.

Choosing the right financial business intelligence tool has a direct impact on how effectively a finance team can manage performance, control costs, and support strategic decisions. The right platform transforms complex financial data into structured insight that CFOs and finance leaders can act on with confidence.
Based on my experience implementing BI solutions for finance departments, three tools consistently stand out: Power BI, Tableau, and Looker. Nearly every organisation I have worked with relied on one of these platforms to build centralised dashboards that act as a single source of truth, ensuring all decision-makers work from the same numbers.
These BI tools integrate with core financial systems such as SAP HANA, Anaplan, and QuickBooks Online, while offering advanced data modelling and visualisation capabilities for custom finance reporting. They also enable CFOs to use predictive modelling and scenario simulations to forecast cash flow, test budget assumptions, and evaluate financial risk. At the same time, enterprise-grade security features such as multi-factor authentication and data encryption protect sensitive financial data across collection, storage, and access.
Below, I will break down the strengths of each tool and share practical insights to help you choose the right solution for your finance team.
Power BI is a Microsoft business intelligence tool that connects to 250+ data sources, costs $14+ per user per month and has excelent data transformation capabilities. In addition to its data integrations, Power BI allows organizations to consolidate financial data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis.
It is most suitable for organizations that rely on other MIcrosoft services like SharePoint, Dynamics, Azure, etc. Using Power BI makes it easy to integrate with other Microsoft tools which saves a lot of time and makes it easier to embed finance BI reports into your daily workflows.
There are also some licensing benefits when you use Power BI along with other Microsoft tools. For example if you have a Microsoft office E5 license, Power BI is free.
Power BI is my personal favorite for financial business intelligence.
Tableau is owned by Salesforce, connects to 150+ data sources, costs $15+ per user per month and is excelent at data visualization. In addition to its visualization strengths, Tableau offers robust data integration capabilities, allowing organizations to consolidate financial data from multiple sources. This integration helps maintain data accuracy in financial reporting by supporting data validation and cleansing processes.
Some Tableau licenses cost closer to $70 per user per month so generally you pay a bit more for Tableau. You primarily pay for more advanced data visualization capabilities as Tableau offers more ways to chart types and ways to customize them.
Tableau is best for organizations that want to create sophisticated data visualizations (which is quite rare in finance since most users prefer simple tables).
The truth is Tableau is probably just as good for financial business intelligence as Power BI. If you are not relying on other Microsoft services and you prefer Tableau you can absolutely choose it for financial BI.
Looker is owned by Google and is an enterprise-level BI tool. The Looker license costs 35k+ per year and the learning curve for it is a bit steeper than with Tableau or Power BI. Looker also offers robust data integration and data warehousing capabilities, making it well-suited for consolidating financial data from various sources and supporting large-scale financial data analysis.
The main advantage of Looker is that it allows multiple developers to work on a dashboard together at the same time.
Admittedly, Looker has many design limitations such as where to put tiles and filters. As a result, if you want to achieve advanced design for your reports, Looker is not the best option for you.
Looker is also a great choice for embedded analytics. It is a great choice if you need to embed dashboards into your internal tools and let users analyze their data.
Business intelligence in financial services refers to the use of business intelligence specifically for financial institutions like banks, investment funds and insurance companies. The main applications of business intelligence in the financial industry are managing investments, monitoring risks and customer segmentation. Business leaders rely on financial insights and data-driven insights from BI tools to guide strategic decisions, improve profitability, and manage risk effectively.
In my practice, I have mainly worked with private equity companies that invest on behalf of their clients and use business intelligence to drive buy or sell decisions. BI dashboards help these companies to report on their performance to clients and decide whether to buy or sell a particular financial asset.
Based on my experience, the most common data sources for this type of analysis include Yahoo Finance, Benzinga, and other financial market data providers..
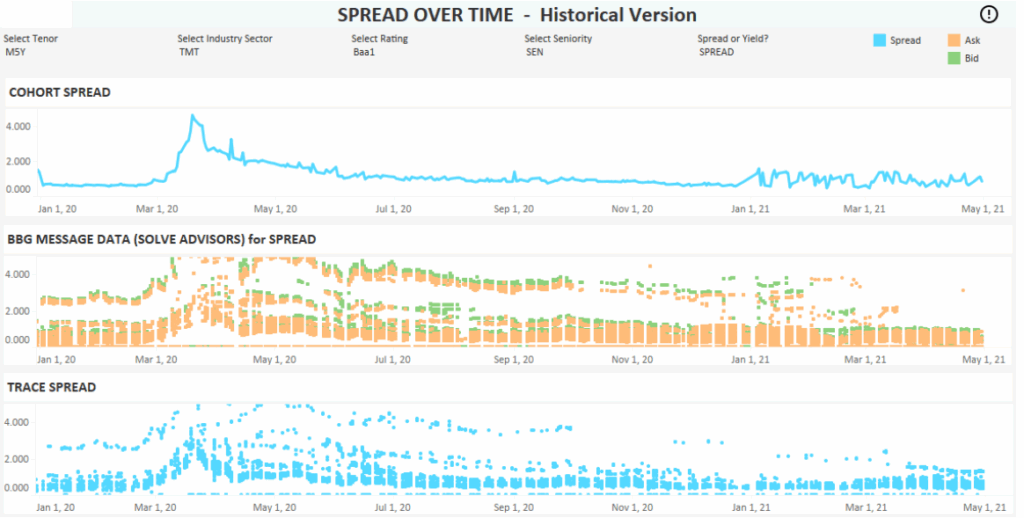
For example, our Tableau developers built the BI dashboard below for a corporate bond investment company. This dashboard helps them to monitor the bid and ask prices of corporate bonds and the difference between the 2.
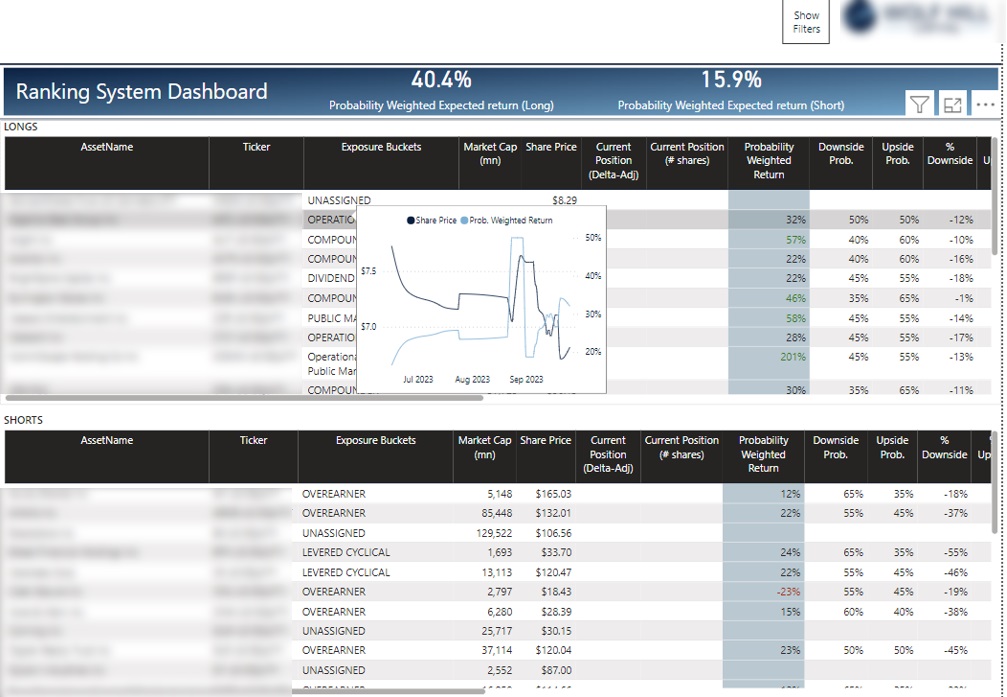
Similarly our Power BI developers have worked with an investment management firm that invested into different stocks on behalf of their clients. The dashboard gives a clear snapshot of assets held in long and short positions as well as all the relevant metrics for them. The investment managers can also hover to a particular asset and see the share price trend. The BI tools that we developed enable finance teams to track financial operations, evaluate
Accounting business intelligence refers to using data analytics and visualization to transform accounting data into management reports. The main goal of business intelligence in accounting is analyzing accounting metrics and ratios to improve the company financial management. This analysis is typically presented to the CEO in small companies and the CFO in larger organizations.
Based on my experience, the data for accounting BI reports usually comes from accounting tools like QuickBooks Online, Xero, Zoho Books, Netsuite and others. BI analysts usually extract the list of transations from these tools which is grouped into general ledger accounts. This data is then used to create accounting dashboards like the one you see below.
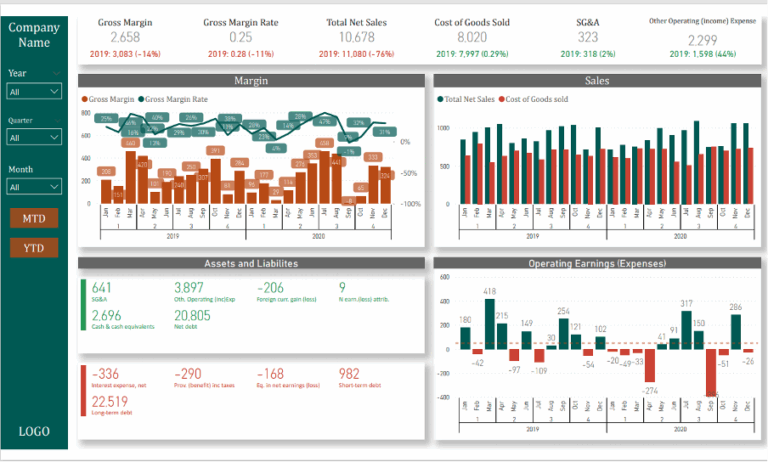
Dashboards like these are usually a good starting point for accounting business intelligence. They usually analyze P&L and Balance Sheet metrics to help finance managers analyze business profitability and any risks.
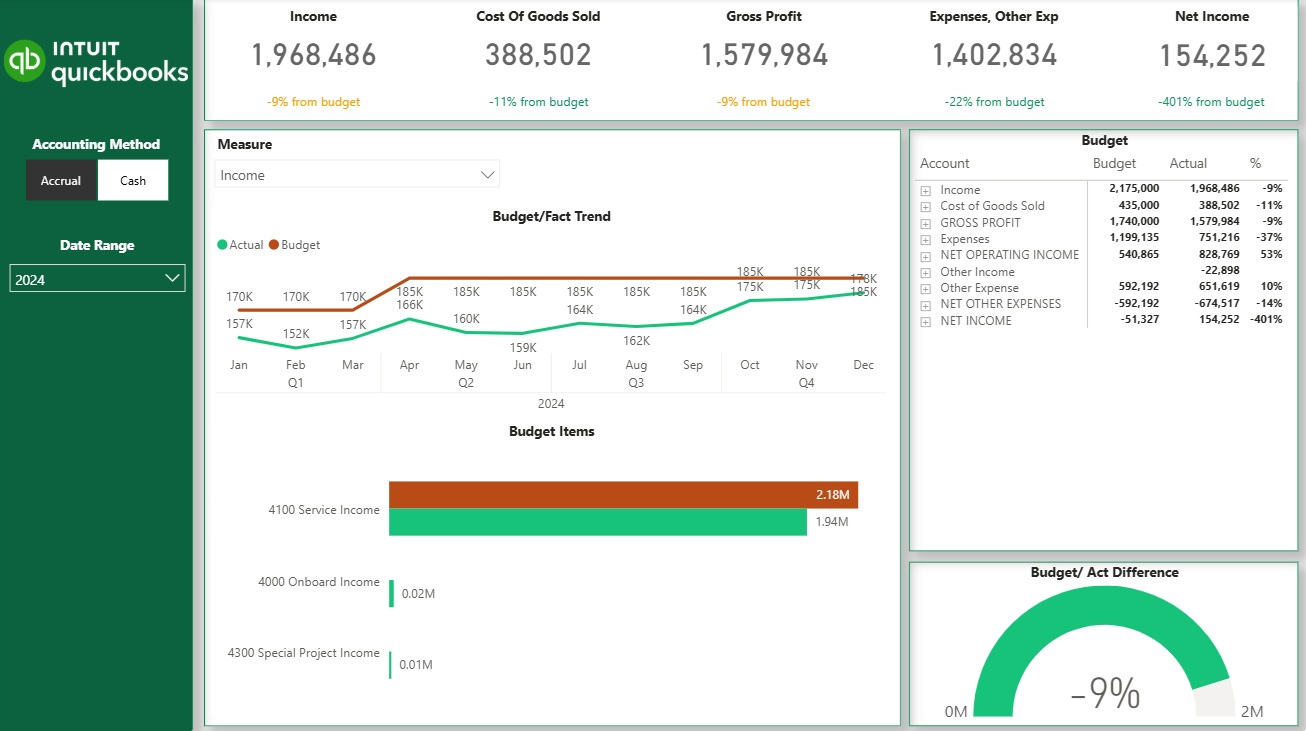
Another example of a common accounting analysis is comparing actuals to budget. Companies usually set budget for every line item in the P&L in the beginning of the year. As the actual performance data becomes available throughout the year, companies compare the actual performance to their targets.
Many companies go a step further and create accounting business intelligence dashboards for individual processes managed by the accounting team.
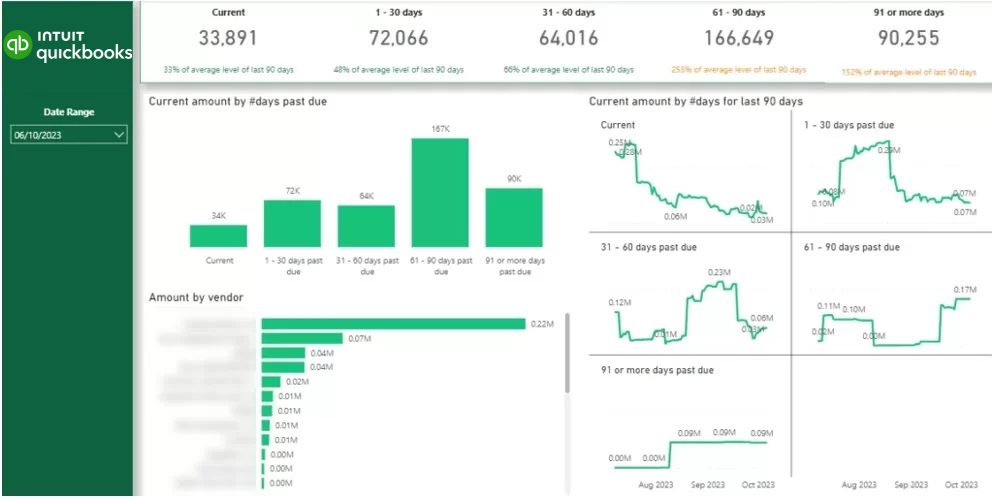
For example, accounting teams are often responsible for managing account receivables and collecting payments quicker on the outstanding invoices. An account recievable dashboard like the one below makes it easy to see which customers owe the money to the company and how long the invoices have been outstanding for.
Credit controllers can then work through the list of customers on the dashboard and contact them one by one to collect payments. The CFO can then monitor the total outstanding balance in the same dashboard to evaluate how efficiently the accounting team collects the outstanding payments.
Large corporations have internal financial analytics teams that produce business intelligence dashboards. Their analysis supports the financial forecasting process and helps to evaluate the sales team performance.
When I produced these dashboards in Autodesk, the finance and sales directors would discuss them together on weekly basis. Finance directors would then adjust their financial forecast based on the performance that they saw in the dashboards and the input from the sales directors on the open deals.
Common data sources for this analysis are ERPs like SAP Hana and Netsuite which contain all the data on actual sales. The data from CRM systems like Salesforce is also often used to analyze the sales pipeline and help with financial forecasting.
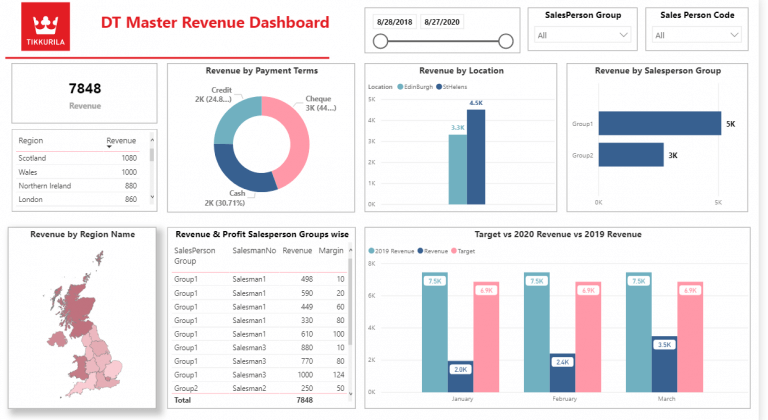
You can see an example of a finance business intelligence dashboard below. It analyzes the company revenue by location, salesperson and sales channel. This analysis can then be used to forecast revenue for every location and sales team.
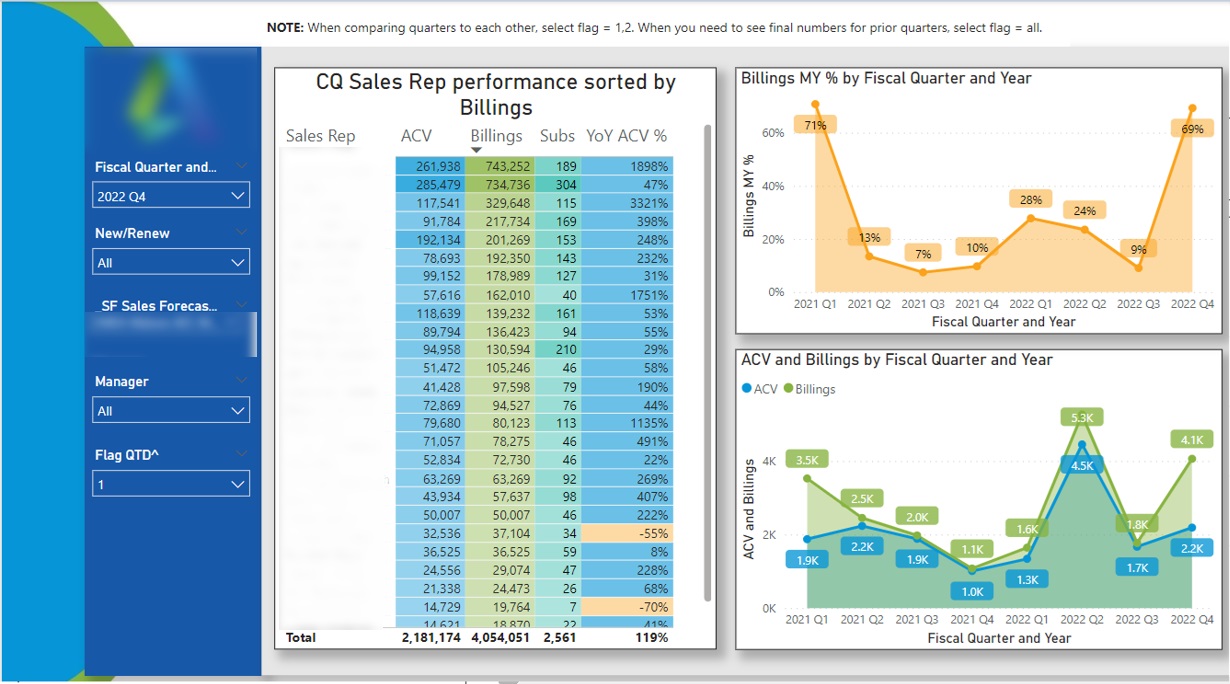
Financial analysts also often support sales teams by analyzing the performance by sales rep. For example the business intelligence dashboard below ranks sales reps by invoiced revenue in a particular quarter and shows how many subscriptions they sold. The sales managers can then click on a sales rep name and see the trends quarterly trends for their performance.
Finally, analyzing the CRM data helps the finance teams in B2B companies to more accurately forecast financial performance.
The CRM data helps to measure the amount of revenue sitting in the sales pipeline and average conversion rate of opportunities into deals. Financial directors can also discuss likelihood of winning individual deals with the sales directors and use this information to more accurately forecast revenue.

BI tools allow businesses to track financial operations, evaluate market conditions, and assess credit risks effectively. They also help analyze how different strategies impact a company’s profitability. By consolidating data and providing data-driven insights, BI tools support informed decision making by delivering accurate, timely information that uncovers hidden patterns and trends.
Additionally, predictive analytics helps businesses forecast future financial performance. Real-time analytics provided by BI tools allow businesses to make data-driven decisions quickly in response to market changes.
By leveraging BI in finance, organizations can enhance data analysis and make higher quality strategic decisions.
For example when we developed CFO dashboards for Neterra Telecommunications they reported finding a one-off cost-saving opportunity worth 50k Euro and finding new business opportunities worth about 10k Euro per month. You can read their review here or view their video testimonial below.
BI tools help reduce manual work by automating data extraction, processing, and reporting. Process automation helps to minimise the risk of errors while saving time and resources. Financial teams can then focus on more high-value tasks.
For example, our consultants implemented business intelligence reports for a financial services company combining the data from QuickBooks Online, Zoho CRM and Excel. These reports are fully automated and save them 10+ working hours per month as they reported in their review.
Traditionally, financial reports are manually refreshed once a week since the process is manual and takes several hours every time. Automating finance reports using BI tools means that you can schedule automated data refresh several times a day bringing the financial reports near real-time. Real-time analytics and data-driven insights provided by financial business intelligence tools enable organizations to respond quickly
Having access to real-time reports is especially important when implementing business intelligence in financial services since the data changes so frequently.
As you can see Business intelligence supports strategic initiatives and financial strategies by providing actionable insights that drive better decision-making, predictive modeling, and scenario planning. Additionally, resource allocation insights in BI help optimize budgets by identifying the highest return on investment customer segments
Now that you know the key benefits of business intelligence in finance, it is important to apply them in the right areas. I listed several common applications of BI in finance based on my experience below.
The use of business intelligence in finance helps to mitigate risks through real-time data analysis and automated alerts. Real time dashboards enable finance teams to increase transparency, detect potential issues early and take preventive action before problems escalate. Automated alerts can flag unusual patterns or compliance violations, helping to reduce the risk of fraud.
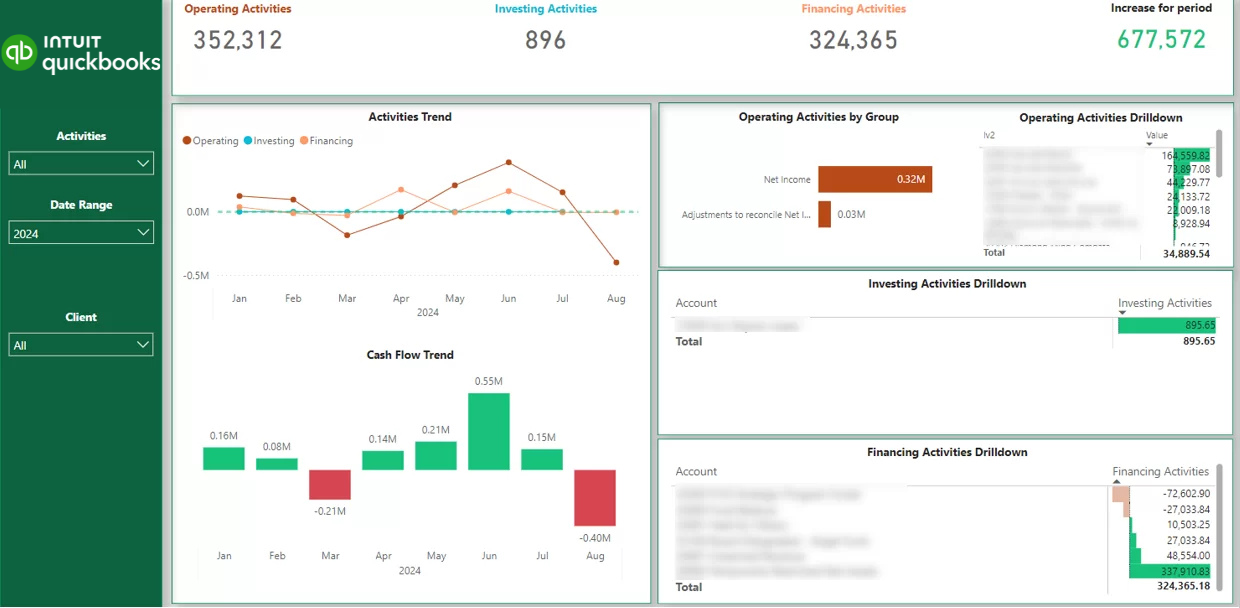
Financial BI reports facilitate cash flow management by providing a real-time view over the current cash flow position and recent changes. This analysis helps financial directors to evaluate affordability of new initiatives and ensure that the cash reserves are sufficient to keep the operations as they are. The dashboards also make it easy to identify the largest business expenses and find the irregular payments.
Financial business intelligence reporting is often focused around the company sales process. In fact, financial analysts often support the sales teams with their analysis, making the sales management more structured and increasing sales. By analyzing customer behavior patterns with BI, companies can improve sales forecasting and develop more effective sales strategies.
For example, financial BI dashboards can be used for identifying which sales accounts grew and shrank over time. The sales reps can then proactively suggest new ideas to the growing accounts and approach the shrinking accounts to offer help.
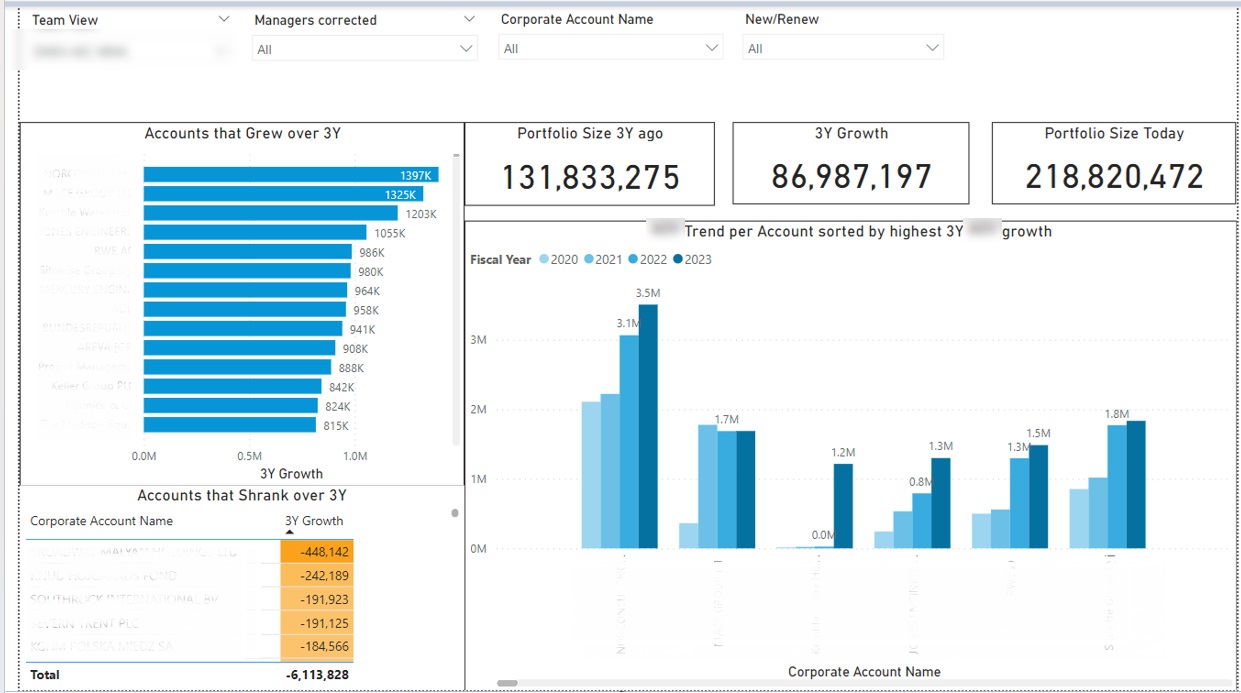
Business intelligence makes the financial reporting process a lot more efficient. This is important because finance teams spend a big portion of their time reporting on financial performance to shareholders and peers.
Automating financial reports using BI tools saves time for report maintenance and enables finance professionals to create more valuable analysis.
Strategic planning is essential for organizations aiming to achieve long-term success, and financial business intelligence plays a pivotal role in this process. By utilizing BI tools, finance teams can analyze market trends, evaluate business performance, and pinpoint areas for improvement. Financial BI enables organizations to develop predictive models that forecast future financial performance, helping leaders anticipate challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
With access to real-time data and advanced analytics, finance teams can track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure progress toward strategic objectives. This data-driven approach to strategic planning ensures that decisions are based on accurate, up-to-date information, allowing organizations to allocate resources effectively and respond proactively to market changes. By integrating financial business intelligence into their strategic planning processes, companies can enhance their ability to achieve business goals, manage risks, and drive sustained growth.
Maintaining regulatory compliance is a critical responsibility for any financial business, and financial business intelligence provides the tools needed to meet these demands.
Implementing financial business intelligence ensures that financial systems and processes are aligned with regulatory requirements, promoting transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. This not only safeguards the organization against compliance breaches but also builds trust with stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to ethical and responsible financial management. With robust BI solutions in place, organizations can streamline compliance efforts, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain a strong reputation in the financial industry.
Like any implementation, financial business intelligence comes with its own set of challenges.such as legacy system integration and managing data complexity. Poor data quality—such as inaccurate, inconsistent, or missing data—can also hinder the effectiveness of BI and must be addressed through data cleaning and integration. Let’’s explore the key obstacles that may hinder adoption and the strategies to effectively overcome them.

One of the biggest barriers to financial business intelligence adoption is fragmented data, stored across multiple systems, formats, and departments. This leads to inconsistent reporting, duplication, and errors in decision-making.
To eliminate data silos, businesses should establish unified data lakes, which consolidate financial information from various sources into a centralized, structured repository. Data warehousing is also essential for storing and managing large volumes of historical financial data, supporting trend analysis, forecasting, and seamless integration within the broader business intelligence and data integration ecosystem.
By unifying financial data, organisations can enhance reporting accuracy, forecasting precision, and operational efficiency.
Organisations must invest in structured learning programs that empower employees with the skills necessary to interpret, analyse, and apply financial intelligence.
Involving key stakeholders and business leaders in training and adoption efforts is crucial to ensure that the needs of all departments are addressed and to drive successful implementation.
Equipping teams with data literacy enhances their ability to make informed decisions and fosters a data-driven corporate culture.
Financial leaders often hesitate to allocate large budgets to this system due to uncertainty in ROI and implementation risks. Many companies fear overinvestment in BI tools without concrete performance gains.
Instead of full-scale implementation, businesses should start with targeted, modular pilots that demonstrate measurable ROI before scaling further.
Aligning BI investments with strategic initiatives and financial strategies ensures that resources are directed toward analytics projects that optimize decision-making and support business growth.
By proving the value of the financial business intelligence through pilot programs, organisations can secure executive buy-in and justify larger-scale investments.
Financial Business Intelligence has become an indispensable tool for modern finance, transforming decision-making, forecasting, cost optimisation, and regulatory compliance. By integrating data analytics, automation, and financial expertise, businesses can gain real-time insights, reduce risks, and drive profitability.
As organisations continue to navigate economic challenges and evolving financial landscapes, embracing this system ensures strategic agility and competitive advantage. Those who invest in scalable BI solutions, data-driven strategies, and financial automation will lead the future of finance with efficiency, accuracy, and innovation.